A professional bag factory audit is a fundamental component of supply chain risk management, serving to protect buyers from product safety hazards and catastrophic recalls. In the softline industry, particularly for luggage and handbags, the presence of metal contaminants like broken needle fragments poses a severe injury risk to consumers. Auditors systematically evaluate a manufacturer's adherence to "Zero Tolerance" safety protocols, focusing on the documentation of broken needle incidents and the rigorous calibration of industrial metal detectors. A comprehensive audit ensures that compliance is not just a policy but a consistent operational reality.

Key Takeaways
- Safety Priority: Metal detection is the final safeguard against consumer injury and legal liability.
- Needle Control: Effective procedures require a "One-for-One" exchange system at a central security point.
- Calibration Standards: The 9-Point Check is the gold standard for verifying metal detector sensitivity across the entire conveyor belt.
- Audit Readiness: Real-time digital logs are superior to paper records for ensuring transparency and preventing retrospective data entry.
- CAPA Framework: A failed calibration or needle incident must trigger an immediate, documented Corrective Action Plan.
The Strategic Role of Quality Management Systems (QMS)
A factory's Quality Management System is the backbone of its production reliability. Auditors begin by evaluating how the facility integrates safety checks into the standard process flow. This includes verifying ISO 9001 compliance and ensuring that quality objectives are measurable and communicated to the workshop floor. Without a robust QMS, even the best metal detection equipment becomes ineffective due to human error and lack of oversight.
| QMS Pillar | Audit Focus | Operational Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Process Control | In-line and final inspection routines. | Documented check-sheets for every batch. |
| Risk Management | Identification of potential safety hazards. | Critical defect classification (Zero Tolerance). |
| Documentation | Traceability of calibration and needle logs. | Daily logs kept for at least 24 months. |
| Personnel Training | Competency of metal detector operators. | Bi-annual training and certification records. |
Broken Needle Procedure: Verification Protocols
The "Broken Needle Procedure" is one of the most strictly scrutinized areas during a factory audit. A loose fragment of a needle can easily be trapped in the thick seams of a leather bag or the padding of a backpack, becoming invisible to the naked eye. Auditors verify that the factory enforces a strict "No Spare Needle" policy at sewing stations.
Technical Steps for Incident Handling
When a needle breaks, the audit verifies that the following SOP is followed without exception:
- Immediate Stoppage: The operator must stop the machine and notify the supervisor immediately.
- Fragment Reconstruction: All pieces of the broken needle must be recovered and taped to an incident report to form a complete needle.
- Isolation: All work-in-progress (WIP) within a 3-meter radius must be quarantined and passed through a specialized needle detector.
- Magnetic Sweeping: The workstation floor must be swept with a high-intensity magnetic bar to catch microscopic shards.
"A missing needle fragment is a critical failure. If 100% of the needle cannot be accounted for, the entire batch of products in that area must be rejected or sent for X-ray scanning."
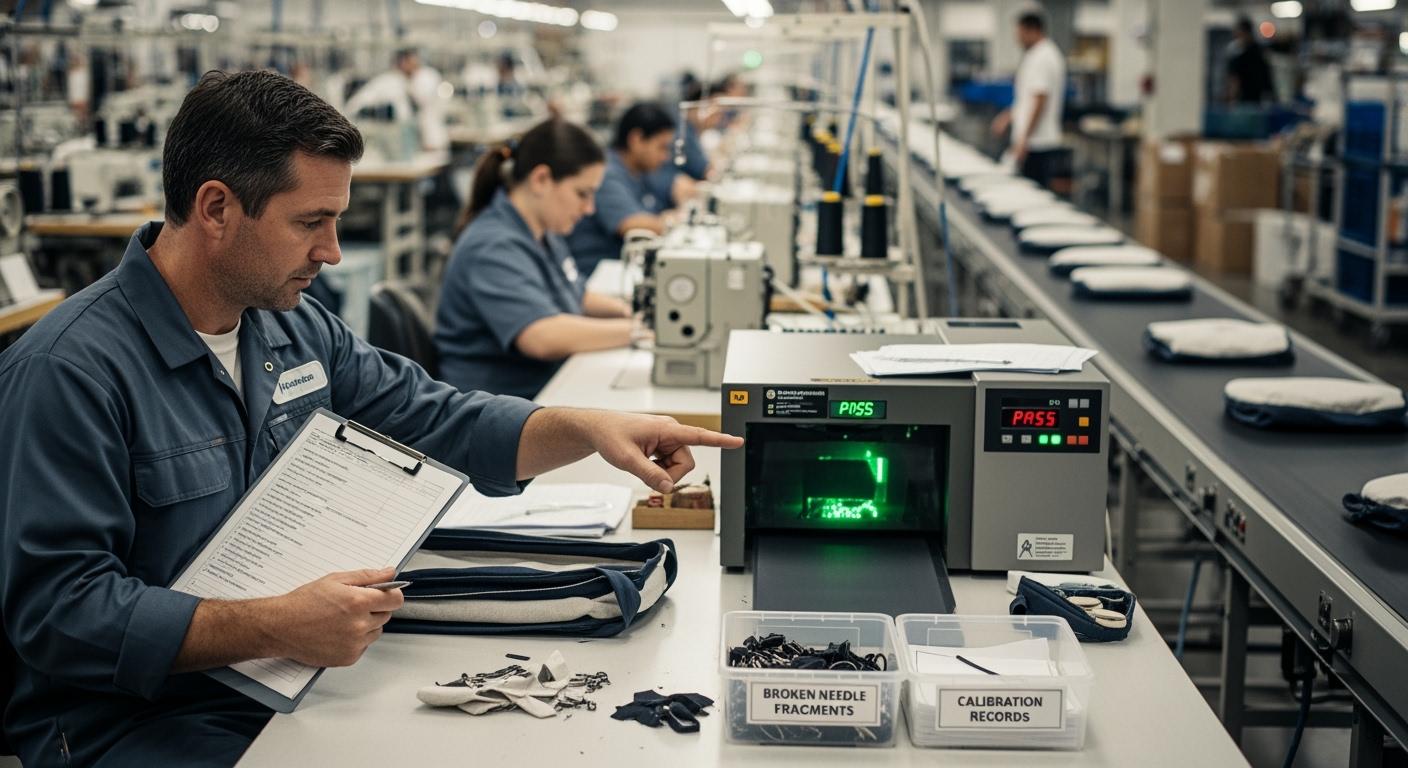
Metal Detection and 9-Point Calibration
Industrial metal detectors are sensitive instruments that require frequent verification. Calibration ensures the machine can distinguish between the 'Product Effect' (the natural conductive properties of the bag's zippers and buckles) and an actual foreign contaminant.
The 9-Point Verification Method
Auditors look for records of the "9-Point Check," which tests the sensitivity of the detector at various heights and positions on the conveyor belt. The detector's sensitivity is often lower at the center-top compared to the edges. A standard 1.0mm to 1.2mm Ferrous (Fe) test card is used for these checks.
| Calibration Zone | Test Frequency | Technical Objective |
|---|---|---|
| Start of Shift | Daily (Before Production) | Validate baseline sensitivity settings. |
| Hourly Checks | Every 60 Minutes | Ensure no "Sensitivity Drift" due to machine heat. |
| End of Batch | After each order completion | Confirm all items passed through a functional unit. |
| Post-Maintenance | After any repair | Re-verify detection threshold after setting changes. |
Digital Reporting and Audit Transparency
The move toward digital audits has significantly increased transparency. Through TradeAider’s factory audit services, clients not only receive an official audit report within 24 hours, but can also view audit progress and key findings during the on-site audit via TradeAider's online service system.
By reviewing the Online Real-time Audit Report, brands gain timely insight into factory capabilities, quality management practices, and compliance risks. This enables informed decisions on supplier qualification, corrective action requirements, and follow-up audits—helping brands strengthen supplier control, reduce sourcing risks, and drive continuous improvement across their supply chain.
Critical Non-Conformity (NC) Management
If an auditor discovers a gap, such as a missing entry in the metal detection failure record, it is categorized as a Major Non-Conformity. The factory must then provide a Corrective Action Plan (CAPA) that identifies the root cause and outlines the steps to prevent recurrence. Auditors will then perform a follow-up visit to "Close the Loop" on these findings.
Internal Audit Readiness Checklist
To prepare for a professional third-party quality assurance audit, bag factories should perform monthly internal reviews. This proactive approach identifies compliance gaps before they become deal-breakers for international buyers. The checklist should include:
- Verification of "Metal-Free Zones" around the detection equipment.
- Inspection of the needle disposal containers (must be sealed and tamper-proof).
- Review of the sensitivity certificates for the test pieces (Test cards must be within their expiration date).
- Observation of a mock needle-break incident to test staff reaction time and SOP adherence.
The Financial Impact of Compliance Failure
Neglecting these procedures can be devastating. A single needle fragment found by a customer in a retail store can lead to millions in product recalls, massive fines from consumer protection agencies, and the permanent loss of major retail contracts. Robust auditing is not just a cost—it is an investment in the brand's survival.
| Risk Category | Description of Threat | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Liability | Consumer injury lawsuits. | Strict adherence to broken needle SOPs. |
| Recall Costs | Shipping and disposal of faulty goods. | 100% metal detection before packing. |
| Brand Reputation | Negative social media and press coverage. | Consistent third-party audits. |
Ready to secure your product quality before shipment?
As your third-party inspection, testing & certification partner in China, TradeAider supports brands and sourcing teams across the entire production process, helping you identify quality risks early, ensure compliance, and strengthen your team’s capabilities before shipment.
Book an Inspection or Testing Service with TradeAider today, or for tailored solutions and expert guidance, contact us at services@tradeaider.com.
FAQ
What is a 9-point metal detection check?
It is a calibration procedure where a test piece is passed through the detector at nine different locations: Left (Bottom, Middle, Top), Center (Bottom, Middle, Top), and Right (Bottom, Middle, Top). This ensures no "blind spots" exist on the conveyor belt.
Why is there a "One-for-One" needle exchange policy?
This prevents operators from having extra needles that could be lost without notice. A worker must present all fragments of a broken needle to the supervisor before receiving a single new replacement needle.
Can a bag with metal zippers pass through a metal detector?
Yes, but it requires "Product Effect" compensation. Modern detectors can be programmed to ignore the specific signal of brass or aluminum zippers while still detecting a high-carbon steel needle fragment.
How long should a factory keep calibration records?
Most international buyers require records to be kept for a minimum of two years. This provides a clear audit trail in the event of a quality dispute or safety claim later in the product's lifecycle.
What happens if a fragment cannot be found?
The product must be quarantined and passed through a highly sensitive X-ray machine. If the fragment still cannot be located, the individual bag must be destroyed to ensure consumer safety.
Grow your business with TradeAider Service
Click the button below to directly enter the TradeAider Service System. The simple steps from booking and payment to receiving reports are easy to operate.




