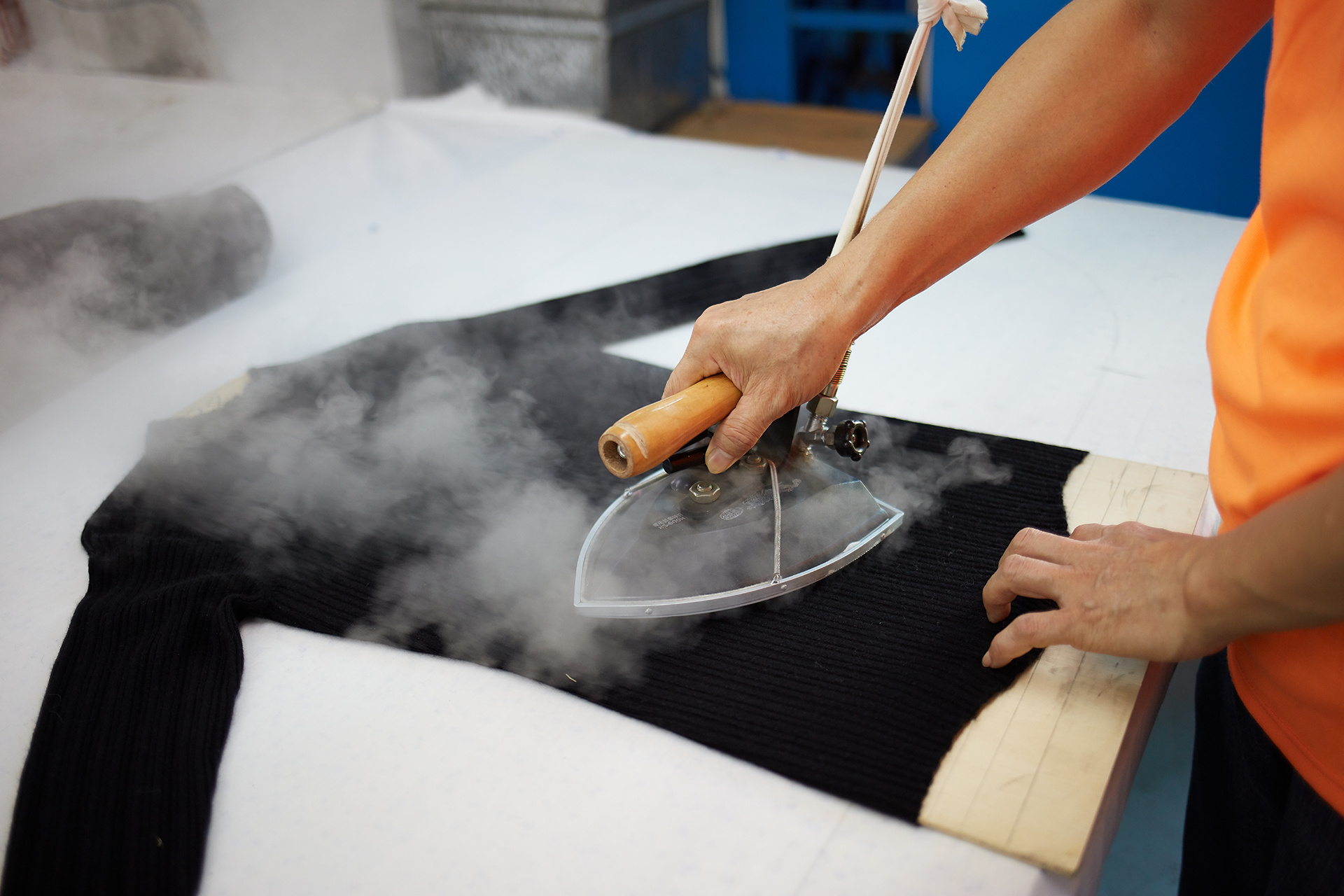
A shirt with a crooked seam or a sweater with uneven color often signals a breakdown in quality control in apparel. The apparel industry relies on strict quality measures to ensure each piece meets exact standards. Quality control in apparel checks every stage, from fabric to finished garment, to prevent defects. High quality remains the goal, as customers expect consistency. Apparel manufacturers use quality control to build trust and maintain a reputation for delivering quality products in a competitive market.

Quality Control in Apparel: Standards
Product Specifications
The apparel industry relies on clear product specifications to guide quality control. These specifications describe every detail of a garment, such as fabric type, color, stitching, and measurements. Quality assurance teams use these details to set quality standards for each product. When workers follow these specifications, they help prevent mistakes and maintain consistency. Quality control in apparel starts with checking if materials and designs match the required standards. For example, a shirt must meet the exact sleeve length and fabric weight listed in the product sheet. If a garment does not meet these standards, quality control teams flag it for review. This process helps the apparel industry deliver products that meet customer expectations.
Note: Product specifications act as a contract between design and production teams. They ensure everyone understands the quality requirements for each item.
Acceptable Quality Levels
Quality control uses acceptable quality levels (AQL) to measure how many defects are allowed in a batch of apparel. The apparel industry sets these levels based on customer needs and market demands. Quality assurance teams inspect samples from each batch to check if they meet the AQL. If the number of defects stays below the set level, the batch passes quality control. If not, the team investigates and takes action to improve quality. This method helps maintain high quality standards across all products. Quality control in apparel depends on strict AQL checks to keep defective items out of the market.
A simple table can show how AQL works:
| Batch Size | AQL (%) | Max Defects Allowed |
|---|---|---|
| 100 | 2.5 | 2 |
| 500 | 2.5 | 12 |
| 1000 | 2.5 | 24 |
Quality assurance and quality control work together to ensure every piece of apparel meets the required standards. This focus on quality helps the apparel industry build trust with customers and maintain a strong reputation.
Pre-Production Inspection
Pre-production inspection stands as a critical step in the apparel industry. This process helps manufacturers catch problems before production begins. Quality control teams focus on materials and samples to ensure every garment meets the required standards. Early inspections save time and resources by preventing defects from reaching later stages.
Fabric and Material Checks
Quality control starts with fabric and material checks. Inspectors examine every roll of fabric for color consistency, texture, and strength. They look for flaws such as stains, holes, or uneven dye. The apparel industry relies on strict inspection protocols to catch these issues early. Quality assurance teams use both manual and automated methods to test materials. For example, they may use machines to measure fabric thickness or test for colorfastness.
Some factories now use AI-powered systems to scan fabrics. These systems can detect tiny defects that human eyes might miss. Technology improves the accuracy of inspections and speeds up the process. Quality control teams record their findings and decide if the materials meet the standards. If the fabric fails inspection, the team rejects it and requests a replacement. This step ensures that only high-quality materials enter the production line.
Tip: Consistent fabric quality reduces waste and helps maintain the reputation of the apparel industry.
Sample Testing
Sample testing forms the next step in pre-production inspection. Quality assurance teams create a small batch of garments using approved materials. They check these samples against product specifications and inspection protocols. Inspectors measure seams, check stitching, and test buttons or zippers. They also wash and stretch the samples to see how they hold up under stress.
The apparel industry values this process because it reveals potential problems before mass production. Quality control teams use the results to adjust the process if needed. For example, if a seam unravels during testing, the team changes the stitching method. Technology plays a role here as well. Some companies use digital tools to compare samples with design files. AI can highlight differences between the sample and the original design.
Sample approval marks the final step before full production. If the samples pass all inspections, the factory moves forward. If not, the team repeats the process until the samples meet quality standards. This careful approach ensures that every garment produced will meet customer expectations.
Note: Early detection of defects during sample testing saves time and money for the apparel industry.
In-Process Quality Control
Inline Inspection
In-process quality control plays a vital role in the apparel industry. Inline inspection happens during garment production, not after. Inspectors check each stage to make sure workers follow quality standards. They look for issues like uneven stitching, incorrect measurements, or fabric flaws. This type of inspection helps catch problems early. When inspectors find a defect, they stop the process and correct it right away. This approach prevents large batches of faulty products.
Quality control teams use random inspections to keep the process fair and thorough. They select garments at different times and from various lines. This method ensures that every part of production meets the required standards. Inline inspection supports quality assurance by keeping the focus on quality at every step. It also reduces waste and saves time.
Tip: Regular random inspections during production help maintain high quality and reduce costly mistakes.
Process Monitoring
Process monitoring involves tracking every step of garment production. Quality control teams watch for any changes that might affect quality. They use checklists and digital tools to record data. This information helps them spot trends or recurring problems. For example, if a machine starts making loose stitches, the team can fix it before it affects many garments.
Random inspections remain important during process monitoring. Inspectors review samples from different stages to confirm that quality standards stay consistent. They also check if workers follow the correct methods. Quality assurance teams use this data to improve training and update procedures.
A simple table can show what process monitoring covers:
| Step | What to Check |
|---|---|
| Cutting | Accurate measurements |
| Sewing | Stitch quality |
| Finishing | Clean seams, no defects |
Process monitoring and in-line inspection work together to ensure every apparel item meets strict quality standards. These steps help the apparel industry deliver reliable, high-quality products to customers.
Post-Production Inspection
Final Product Checks
After production, quality control teams perform a final inspection to confirm that each apparel item meets all standards. Inspectors examine garments for defects such as loose threads, uneven seams, or incorrect sizing. They check that every detail matches the product specifications. This step ensures that only garments with high product quality reach customers.
Quality assurance staff use checklists to guide their inspection. They often look for:
• Accurate measurements
• Consistent stitching
• Proper color matching
• Secure buttons and zippers
Inspectors may use measuring tools and visual checks. They also test the durability of fasteners and trims. If they find defects, they separate those items for further review. The final inspection acts as the last defense against poor quality in apparel manufacturing.
Note: Consistent final product checks help maintain high standards and protect the reputation of the apparel industry.
Packaging and Labeling
Once garments pass the final inspection, quality control teams focus on packaging and labeling. Proper packaging protects apparel from damage during shipping and storage. Inspectors check that each item is folded correctly and placed in the right packaging. They also verify that labels show accurate information, such as size, care instructions, and country of origin.
A simple table shows what inspectors review during this stage:
| Packaging Element | What to Check |
|---|---|
| Folding | Neatness, consistency |
| Bags/Boxes | Clean, undamaged |
| Labels | Correct information |
Quality assurance teams ensure that packaging meets all standards. They know that clear labeling helps customers make informed choices. Proper packaging and labeling support overall product quality and customer satisfaction in the apparel industry.
Defects and Improvement
Handling Defects
Quality control teams in the apparel industry must address defects quickly to maintain high standards. They identify defects such as loose threads, uneven seams, or color mismatches during inspections. Workers separate defective items from acceptable ones. This step prevents faulty apparel from reaching customers and protects customer satisfaction.
A typical process for handling defects includes:
1. Detecting defects during inspection.
2. Recording the type and location of each defect.
3. Removing defective items from the production line.
4. Repairing or discarding items based on severity.
Quality management processes require teams to analyze defect patterns. They look for root causes, such as machine errors or incorrect techniques. Teams then update training or adjust equipment to prevent future issues. This approach supports continuous improvement and ensures consistent quality.
Note: Quick action on defects helps maintain product quality and boosts satisfaction among customers.
Continuous Feedback
Continuous improvement relies on feedback from every stage of production. Quality control teams collect data on defects, process efficiency, and customer satisfaction. They use this information to refine methods and set new quality goals. Regular meetings allow teams to discuss trends and share solutions.
A feedback loop in apparel manufacturing often includes:
• Gathering defect reports from inspections.
• Reviewing customer satisfaction surveys.
• Updating quality standards based on findings.
Technology now plays a role in feedback collection. Digital tools track defects and monitor quality in real time. Teams use this data to make informed decisions and drive continuous improvement. This focus on feedback ensures that apparel companies meet changing customer needs and deliver high-quality products.
Tip: Continuous improvement and feedback help the apparel industry adapt and maintain customer satisfaction.
Quality control in apparel involves several key steps, from material checks to final inspections. Each stage helps ensure customer satisfaction by catching defects early and maintaining high standards. Technology now supports teams in tracking issues and improving processes. Continuous improvement leads to better satisfaction and fewer returns. Strong quality control builds trust and supports long-term customer satisfaction in the apparel industry.
FAQ
What is the main goal of quality control in apparel?
Quality control aims to ensure every garment meets set standards for appearance, fit, and durability. Teams check each step to catch defects early. This process helps companies deliver reliable products that satisfy customers.
How do inspectors check fabric quality?
Inspectors examine fabric for color, texture, and strength. They use both manual checks and machines. Some factories use AI systems to spot tiny flaws. Early detection helps prevent problems during production.
Why is sample testing important before mass production?
Sample testing helps teams find design or material issues before making large batches. Inspectors test seams, buttons, and fabric strength. This step saves time and money by preventing widespread defects.
What happens to defective garments found during inspection?
Workers separate defective garments from good ones. Teams record the type of defect and decide if repairs are possible. If not, they remove the item from the batch. This process keeps only high-quality products for customers.
How does technology improve quality control in apparel?
Technology speeds up inspections and increases accuracy. Digital tools track defects and monitor production in real time. AI systems can detect small flaws that humans might miss. These advances help maintain high standards in the apparel industry.