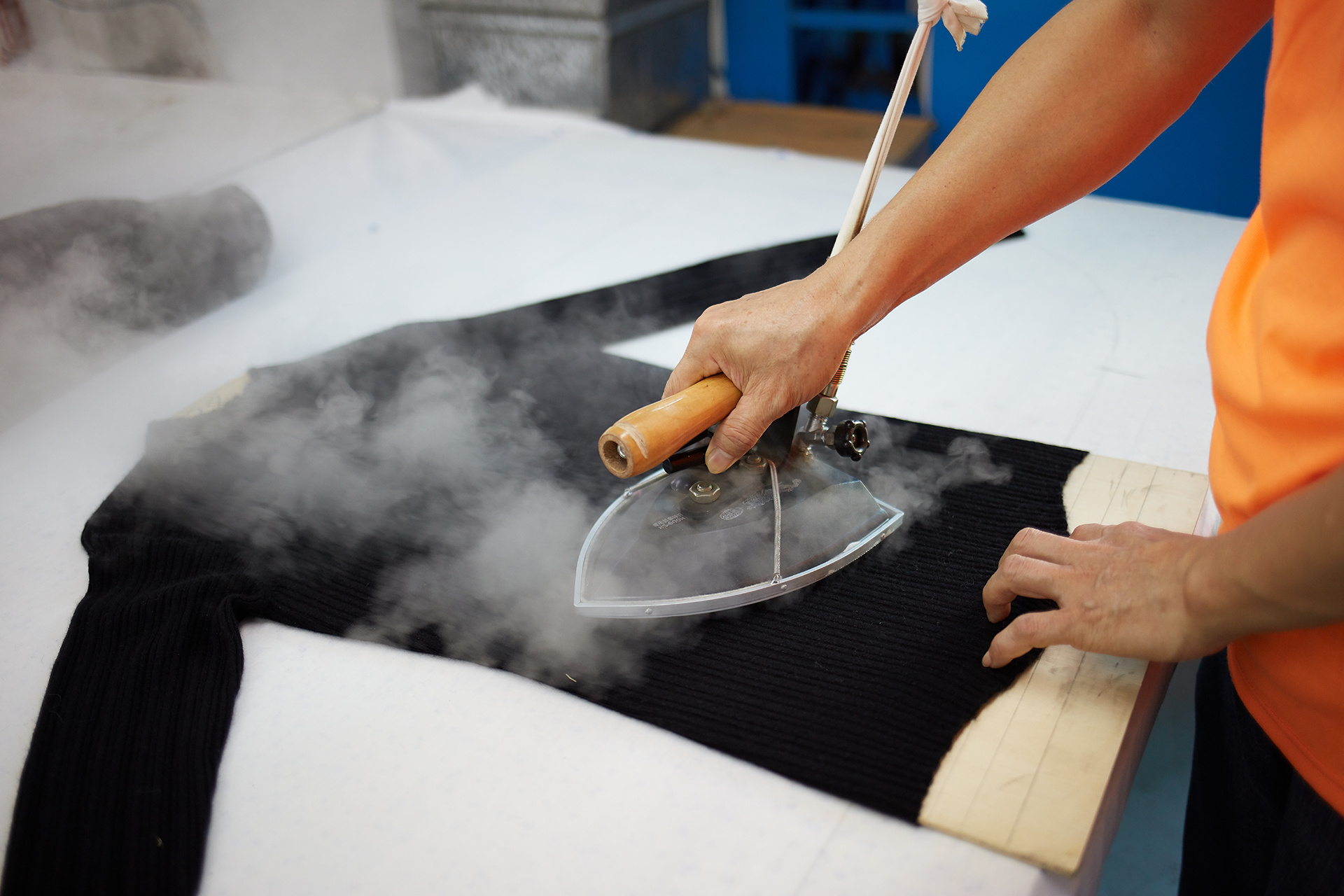
Apparel quality control refers to the process that maintains high standards in the apparel industry. This process checks every stage from fabric selection to the finished product. Quality control helps manufacturers deliver apparel that meets expectations for appearance, durability, and comfort. Consumers rely on quality control to get garments free from defects. The apparel industry uses strict quality guidelines to protect both brand reputation and customer satisfaction. Quality plays a key role in every step of apparel production. Factories monitor quality to reduce waste and improve efficiency. The apparel industry depends on consistent quality to stay competitive. Apparel quality control supports the entire industry by building trust and ensuring reliable products. Quality remains the focus for everyone who values well-made apparel.
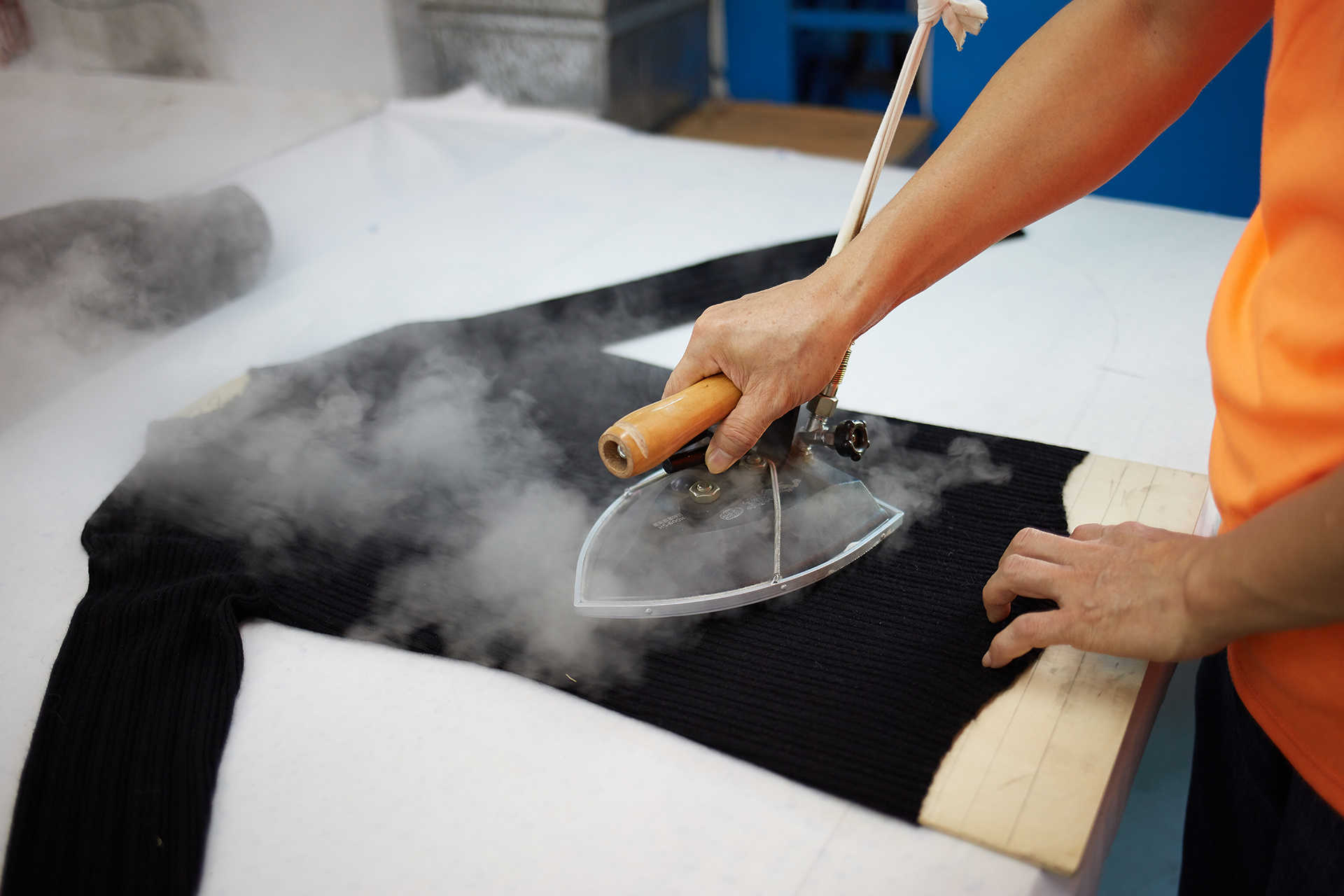

Apparel Quality Control Basics
What Is Apparel Quality Control
Apparel quality control refers to the organized process that ensures garments meet specific standards during clothing manufacturing. This process covers every stage, from raw materials to finished apparel. Factories use quality control to check fabric, stitching, and construction. Inspectors look for defects and measure garments to confirm they match the required specifications. The apparel industry relies on quality assurance throughout the process to maintain consistency. Standards guide each step, helping workers identify and correct problems early. Clothing manufacturing depends on these standards to deliver reliable products. Quality assurance teams use checklists and testing methods to verify that each item meets expectations. They document results and report any issues to management. This approach helps the apparel industry avoid costly mistakes and maintain high levels of quality.
Why It Matters
Quality control plays a vital role in clothing manufacturing. It protects the reputation of the apparel industry by ensuring that only high-quality garments reach consumers. When factories follow strict standards, they reduce the risk of defects and returns. Quality assurance also improves efficiency in manufacturing by catching problems before they become bigger issues. Consistent quality builds trust with buyers and supports long-term business success. The apparel industry faces strong competition, so maintaining high standards is essential. Quality assurance teams help companies meet customer demands for comfort, durability, and appearance. They also ensure that clothing manufacturing follows safety and regulatory requirements. By focusing on quality, manufacturers can deliver products that stand out in the market. Quality control remains a key factor in the success of any apparel business.
Quality Control in Clothing Manufacturing
Standards and Specifications
Quality control in clothing manufacturing starts with clear standards and specifications. These standards set the foundation for every step in the process. Organizations such as the American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists (AATCC) create guidelines that help factories maintain high quality. Standards define what makes a garment acceptable. They cover fabric strength, colorfastness, stitching, and measurements. Specifications give detailed instructions for each product. Workers use these documents to check if garments meet the required quality.
Factories follow quality standards and regulations to ensure safety and consistency. Regulations protect both workers and consumers. They require factories to use safe materials and proper methods. Quality assurance teams review standards before production begins. They compare finished garments to the original specifications. This step helps prevent mistakes and ensures that every item meets the same level of quality.
Note: Standards and specifications guide every decision in clothing manufacturing. They help workers understand what to look for during inspection.
Inspection Steps
A robust inspection process is essential for quality control in clothing manufacturing. Factories use several inspection steps to catch problems early. The inspection process usually includes three main stages:
1. Fabric Inspection
Workers check raw materials before production. They look for defects such as holes, stains, or uneven dye. This step ensures that only high-quality fabric enters the manufacturing process.
2. In-Line Checks
Inspectors monitor garments during production. They check stitching, seams, and measurements. In-line checks help catch errors before they reach the final stage. This step supports continuous quality assurance.
3. Final Inspection
The last step in the inspection process happens after production ends. Inspectors review finished garments for appearance, fit, and construction. They compare each item to the original specifications. Only garments that pass this robust inspection process move to packaging and shipping.
A robust inspection process reduces waste and improves efficiency. It also helps factories meet quality standards and regulations. Quality assurance teams document each inspection step. They use checklists to track results and report any issues.
Testing Methods
Testing methods play a key role in quality control in clothing manufacturing. Factories use different methods and techniques for effective quality control. These tests check if garments meet quality standards for strength, durability, and safety.
Common testing methods include:
• Tensile Strength Test
This test measures how much force fabric can handle before breaking. It ensures that garments will last during normal use.
• Colorfastness Test
Inspectors check if colors stay true after washing or exposure to sunlight. This test helps maintain the appearance of apparel.
• Shrinkage Test
Factories test how much fabric shrinks after washing. This step ensures that garments keep their shape and size.
• Seam Strength Test
This test checks if seams can withstand pulling and stretching. Strong seams improve the overall quality of garments.
• Chemical Safety Test
Factories test for harmful substances in fabrics. Regulations require safe materials in clothing manufacturing.
The inspection process uses these testing methods to confirm that garments meet all quality standards. Quality assurance teams record results and take corrective action if needed. Testing methods help factories deliver safe, reliable, and high-quality apparel to consumers.
Tip: Regular testing and a robust inspection process help factories maintain high standards in clothing manufacturing.
Quality Control Clothing Principles
Consistency
Consistency stands as one of the key elements of quality control in the clothing industry. Workers follow the same procedures for every batch of garments. This approach helps maintain uniform quality across all products. Factories use clear standards to guide each step. These standards cover fabric selection, stitching, and finishing. Consistent processes reduce the risk of defects. Customers expect the same level of quality with every purchase. Quality control clothing teams check for consistency during inspections. They compare samples to approved standards and make sure every item matches the required quality.
Documentation
Accurate documentation supports quality control clothing efforts. Workers record inspection results, test data, and any issues found during production. This information helps managers track quality over time. Factories use documentation to prove they meet industry standards. Detailed records allow teams to identify trends and prevent future problems. Quality control teams rely on documentation to review past performance. They use this data to improve processes and maintain high quality. Proper documentation also supports quality assurance by providing evidence of compliance.
Note: Good documentation makes it easier to trace problems and take action quickly.
Corrective Action
Corrective action forms a vital part of quality control clothing. When teams find defects or deviations from standards, they act fast to fix them. Workers may adjust machines, retrain staff, or change materials. The goal is to restore quality and prevent the same issue from happening again. Quality control teams document each corrective action. They review the effectiveness of these actions and update standards if needed. This process helps factories maintain high quality and meet customer expectations.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement drives long-term success in quality control clothing. Teams regularly review processes and look for ways to raise quality. They use feedback from inspections, testing, and customer reports. Factories set new goals and update standards to reflect best practices. Workers receive training to support ongoing improvement. Continuous improvement ensures that quality control adapts to new challenges in the apparel industry. This principle helps companies deliver better products and stay competitive.
Tip: Continuous improvement keeps quality control clothing systems strong and responsive to change.
Quality Control in Garment Production Challenges
Common Issues
Quality control in garment production faces several challenges. Factories often encounter fabric defects such as holes, uneven dye, or weak fibers. These problems can lower the quality of finished garments. Measurement errors also occur during manufacturing. Workers may cut fabric incorrectly or sew seams that do not match the required standards. This leads to garments that do not fit as intended. Contamination presents another issue. Dust, oil, or foreign materials can affect the appearance and safety of garments. Factories must also follow strict regulations to ensure safe and high-quality products. Sometimes, workers may overlook small defects during inspection, which can result in customer complaints. Inconsistent application of standards can cause variations in quality between batches. Manufacturing processes that do not follow established standards may produce garments that fail to meet customer expectations.
Note: Common issues in quality control in garment production can impact both efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Solutions
Factories use several strategies to overcome these challenges. They set clear standards for every step of manufacturing. Workers receive training to understand these standards and apply them consistently. Regular inspection helps catch defects early. Factories use checklists to guide workers during each stage of production. Automated machines can improve accuracy and reduce measurement errors. To prevent contamination, factories keep work areas clean and use protective covers for materials. Quality control teams monitor compliance with regulations and update procedures as needed. They document all findings and corrective actions. Feedback from customers and regular reviews help factories improve their processes. By following strict standards and regulations, factories can maintain high quality in apparel manufacturing.
Tip: Consistent training and regular updates to standards help factories adapt to new challenges in quality control in garment production.
Apparel quality control shapes the foundation of the clothing industry. It covers every step, from fabric inspection to finished garments. Quality ensures that products meet standards for safety, durability, and appearance. Manufacturers who focus on quality protect their business and build trust with customers.
Ongoing attention to quality helps companies improve and adapt to new challenges.
• Quality control remains essential for product integrity and long-term success in apparel manufacturing.
FAQ
What does apparel quality control check for?
Apparel quality control checks for defects in fabric, stitching, color, and measurements. Inspectors look for problems that affect appearance, fit, or durability. They compare each item to set standards to ensure every garment meets quality expectations.
How often do factories perform quality inspections?s
Factories perform inspections at several stages. They check raw materials, monitor production, and review finished garments. Regular inspections help catch problems early and keep quality consistent.
Why do factories use testing methods in quality control?
Testing methods help factories measure fabric strength, colorfastness, and safety. These tests confirm that garments can handle normal use and meet safety rules. Testing supports reliable and high-quality products.
What happens if a garment fails quality control?
If a garment fails quality control, workers remove it from the production line. They may fix the problem or discard the item. Factories record the issue and take steps to prevent it from happening again.