
Manufacturers rely on precise quality control to ensure metal keychains and badges remain durable and visually appealing. The longevity of these accessories depends heavily on the quality of their plating. A robust plating layer not only enhances the product's finish but also protects the underlying metal from corrosion and wear. Keychains designed for daily use must withstand friction and environmental exposure, making rigorous testing for plating thickness and rust resistance essential for customer satisfaction and brand reputation.

Key Takeaways
- Plating thickness between 1.5 µm (microns) and 2 µm is often ideal for standard metal keychains to balance cost and durability.
- Routine inspections for surface quality and plating uniformity prevent common defects like peeling and spotting.
- Salt spray rust testing is the industry standard for verifying corrosion resistance, ensuring products can withstand humid environments.
- Using calibrated XRF gauges provides non-destructive and accurate measurement of plating layers.
- Buyers should always request third-party lab reports to confirm compliance with safety standards like REACH and CPSIA.
Plating Thickness Measurement for Keychains

Dimensional and Surface Testing
While basic dimensional checks confirm size and weight, plating thickness measurement is critical for assessing longevity. This process evaluates the protective layer applied to the metal substrate. A sufficient plating thickness is the primary defense against tarnishing and oxidation.
Inspectors also perform visual checks for surface defects. Common issues include rough edges, pitting, and uneven coating distribution. Ensuring a smooth, defect-free surface is a prerequisite for accurate thickness testing.
Note: Thicker plating significantly reduces tarnishing and extends the lifespan of outdoor-use products.
Plating Thickness Gauge Methods
Selecting the correct measurement method is vital. The most common techniques include X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) and destructive cross-sectioning.
| Method | Type | Destructive? | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) | Spectroscopic | No | Quick, accurate measurement of multiple layers and composition. |
| Beta Backscatter | Radiometric | No | Measuring precious metal thickness (e.g., gold on nickel). |
| Mechanical Cross Sectioning | Microscopic | Yes | Ultimate referee method for dispute resolution. |
XRF is widely preferred in QC because it is fast, non-destructive, and can measure multi-layer coatings (e.g., gold over nickel over copper). For reliable quality control, the repeatability and reproducibility (R&R) of the gauge should be 10% or lower.
Surface Quality and Enamel Keychains
Enamel keychains require specific attention to the interaction between the metal plating and the enamel fill. Inspectors examine the product for "bleeding" where enamel spills over metal lines, or air bubbles trapped within the enamel.
| Feature | Hard Enamel | Soft Enamel |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Finish | Smooth & Polished Flat | Textured & Recessed |
| Durability | Excellent (Scratch-resistant) | Very Good |
| Cost | Higher | More Cost-Effective |
Common defects in plated enamel products include:
- Oxidation spots on the metal plating.
- Under-filled enamel areas causing a concave surface.
- Dust or debris embedded in the enamel.
Salt Spray Rust Testing for Keychains
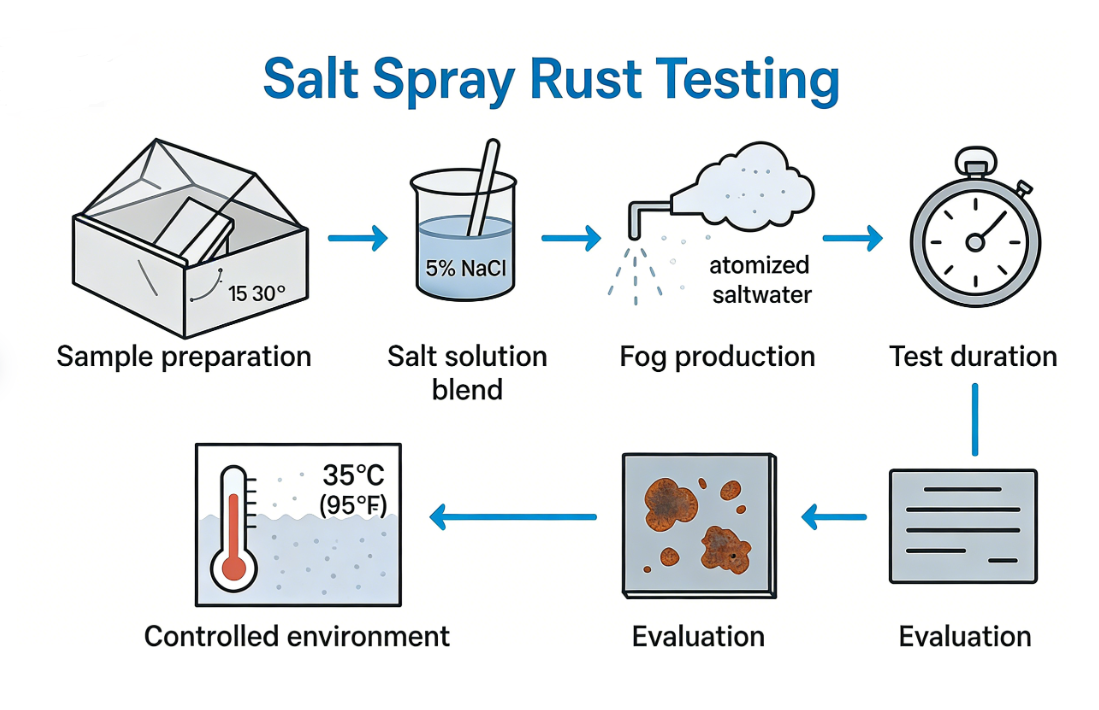
Corrosion Resistance Testing
Salt spray testing is the standard accelerated corrosion test for hardline products. It simulates years of environmental exposure in a short period (usually 24 to 48 hours). This test is crucial for verifying that the protective plating (zinc, nickel, chrome, etc.) effectively seals the base metal from moisture and salt.
International standards like ASTM B117 and ISO 9227 guide the testing parameters, ensuring global consistency.
Salt Spray Test Procedure
The test involves placing the keychains in a closed chamber and subjecting them to a continuous spray of 5% sodium chloride (salt) solution.
- Preparation: Clean samples thoroughly to remove grease or fingerprints.
- Setup: Suspend samples in the chamber without touching each other.
- Exposure: Run the saline fog cycle for the specified duration (e.g., 24 hours).
- Evaluation: Inspect for red rust (base metal corrosion) or white rust (zinc corrosion), blistering, and peeling.
| Test Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ASTM B117 | Standard practice for operating salt spray (fog) apparatus. |
| ISO 9227 | Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres. |
Interpreting Results
Results are typically graded. A common requirement for high-quality keychains is to withstand a 24-hour neutral salt spray test (NSS) with a rating of 9 or higher (minimal corrosion).
The relationship between coating thickness and corrosion resistance is often linear for sacrificial coatings like zinc: doubling the thickness roughly doubles the protection time. However, for barrier coatings, pore-free application is just as important as thickness.
Best Practices for Reliable Testing
Selecting the Right Gauge
Accuracy is paramount. Manufacturers should use gauges that comply with ISO standards. For keychains with complex shapes or enamel fills, XRF is preferred because it can focus on a tiny spot without needing a flat surface area.
Quality Control Protocols
Effective QC protocols involve monitoring the electroplating bath parameters (current density, pH, temperature) to ensure consistent deposition. Regular random sampling for thickness verification prevents batch-wide failures.
| Certification | Focus Area |
|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality management systems. |
| CPSIA | Lead content limits (crucial for children's items). |
| REACH/RoHS | Chemical safety (limits on Nickel release, Cadmium). |
Reliable quality control protects both the manufacturer and the buyer. By implementing rigorous plating thickness checks and salt spray tests, brands can avoid costly returns and ensure their metal accessories stand the test of time. Documenting these QC steps builds trust and verifies compliance with global safety regulations.
FAQ
What is the ideal plating thickness for metal keychains?
For standard durability, a thickness of 1.5 µm to 2 µm is recommended. High-end or outdoor items may require thicker plating for enhanced corrosion resistance.
How does salt spray rust testing work?
It exposes the product to a corrosive saline mist in a controlled chamber for a set period (e.g., 24 hours) to accelerate corrosion and verify the coating's protective qualities.
Why is XRF preferred for testing keychains?
XRF (X-Ray Fluorescence) is non-destructive, fast, and capable of measuring the thickness of multiple coating layers on small, irregular surfaces typical of keychains.
Which certifications matter for metal keychains?
Important certifications include ISO 9001 for general quality, CPSIA for lead safety (US market), and REACH/RoHS for chemical compliance (EU market).
Grow your business with TradeAider Service
Click the button below to directly enter the TradeAider Service System. The simple steps from booking and payment to receiving reports are easy to operate.


.png)