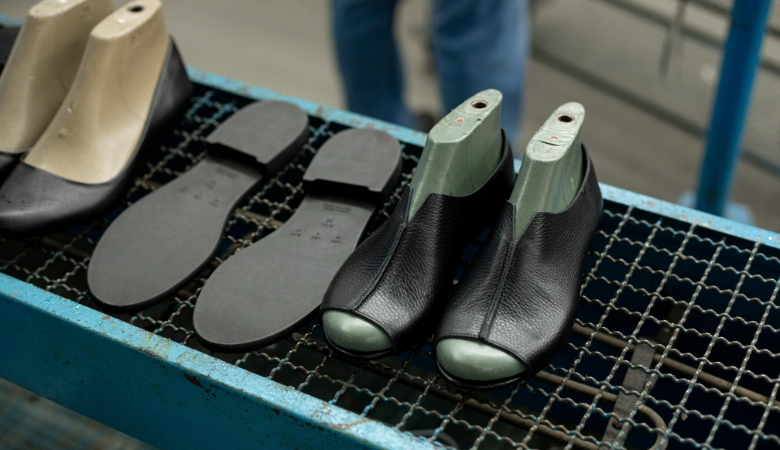
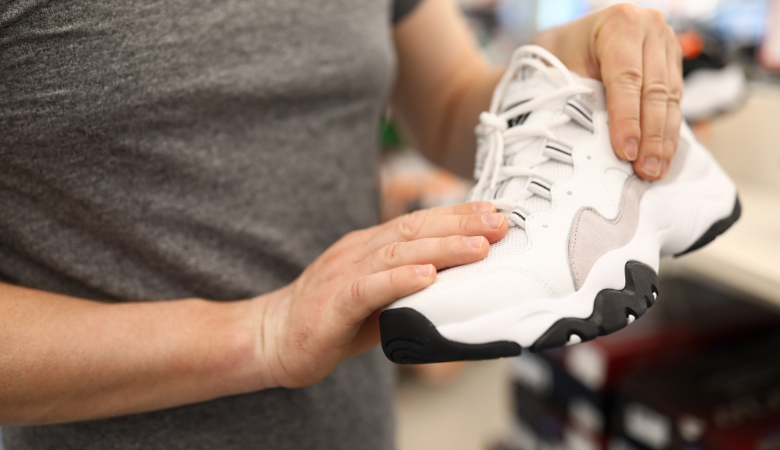
Quality control is the cornerstone of successful garment production.
Quality control ensures that products meet specified standards, satisfy customer expectations, and comply with relevant regulatory requirements. In an industry where brand reputation hinges on consistency and quality, implementing an effective quality control process is crucial for maintaining a competitive edge.
Failure to meet quality standards may lead to product returns, negative reviews, and loss of customer trust. Conversely, high-quality clothing helps cultivate brand loyalty, enhance market position, and reduce production waste. A sound quality control strategy can safeguard brand reputation and drive long-term success.

1. Understand clothing quality control
Definition and objectives of garment quality control
Clothing quality control refers to a series of systematic and scientific management measures and technical means to comprehensively ensure that clothing products meet predetermined standards in terms of design, fit, material selection, and functional performance. The ultimate goal of the process is to minimize product defects, maintain product consistency and stability, and ensure that clothing products comply with relevant safety standards and industry regulations, thereby gaining the trust and satisfaction of consumers.
When delving into the discussion of garment quality control, we cannot avoid mentioning the key factors that influence garment quality. These factors collectively form the cornerstone of high-quality garments.
Key factors influencing clothing quality
• Material selection: Material is the soul of clothing, and high-quality fabrics and accessories are the prerequisite for creating excellent clothing. From natural fibers to synthetic fibers, from the feel of the fabric to its durability, every material choice requires rigorous screening and testing. Only by ensuring that the materials meet the design requirements can we lay a solid foundation for subsequent processing and production.
• Production process: An efficient production process is a crucial aspect of garment quality control. By optimizing the production workflow and adopting advanced production equipment and technology, production efficiency can be enhanced, while ensuring that every garment maintains consistent quality and is defect-free. This not only boosts the market competitiveness of the products but also reinforces consumers' trust in the brand.
• Craftsmanship: Skilled workers are an indispensable part of garment quality control. With their rich experience and exquisite craftsmanship, they can pay attention to every detail and ensure that every garment meets quality standards. Whether it's sewing, ironing, or packaging, each step requires meticulous operation by workers to produce a perfect finished product.
• Compliance standards: Compliance with global and regional regulatory standards is a necessary condition for clothing products to enter the market. From safety performance to environmental requirements, from labeling to packaging specifications, every aspect must strictly adhere to relevant laws and regulations. Only by ensuring product compliance can we smoothly enter the market and win the recognition and favor of consumers.
2. Quality control stage in garment production
Quality control in garment production can be divided into multiple stages, each of which is crucial.
Pre-production planning and material inspection
Before production officially begins, a series of meticulous planning and inspection tasks are indispensable.
• Material quality inspection: The first step in quality control, ensuring that the selected fabrics and accessories meet design specifications and quality standards. Through rigorous inspection procedures, materials with defects or non-compliance can be screened out, avoiding quality issues during the production process.
• Sample review: Before mass production, it is crucial to verify the accuracy of the sample and design. Sample review ensures the accurate conveyance of design concepts, identifies and corrects potential design flaws, and lays a solid foundation for the subsequent production process.
• Trial production: Trial production is one of the crucial stages in pre-production planning. Through small-scale trial production, potential production issues such as unsmooth technological processes and equipment malfunctions can be identified, and timely adjustments and optimizations can be made to ensure the smooth progress of the formal production process.
Monitoring during the production process
Once production officially begins, continuous process monitoring becomes the core of quality control.
• Process inspection: During the production process, it is crucial to conduct real-time monitoring of key production stages. Through process inspection, defects in the production process can be promptly identified and corrected, ensuring that every product meets quality standards. Process inspection can also help production personnel promptly identify and solve problems in the production process, improving production efficiency.
• Size verification: The size of clothing is a crucial aspect that consumers pay close attention to. During the production process, strict verification of clothing sizes is indispensable. Through size verification, it can be ensured that the size of each piece of clothing meets the specification requirements and satisfies the needs of consumers.
Final inspection and quality assurance
When production nears its end, final inspection becomes the last line of defense to ensure product quality.
• Random sampling: Conducting representative spot checks on completed products is a crucial step in the final inspection process. Through random sampling, the quality level of the entire batch of products can be verified, ensuring that every product meets the quality standards. Random sampling also aids quality control personnel in identifying potential quality issues and taking timely measures for rectification.
• Packaging and Display: Before products are shipped, proper packaging and display also constitute a part of quality control. Ensuring that garments are folded correctly, labeled clearly, and packaged appropriately can protect products from damage during transportation and storage, while enhancing the overall image and value of the products.
Post-production audit
After production is completed, auditing serves as a summary and reflection of the entire production process.
• Production report review: By reviewing production reports, we can analyze data from the production process, identify existing issues, and pinpoint areas for improvement. This aids quality control personnel in understanding the overall situation of the production process and provides valuable references for future production.
• Feedback integration: Utilizing feedback information from the production process can enhance future production workflows. By integrating feedback opinions, quality control personnel can propose improvement measures for existing issues, optimize production techniques and processes, and enhance product quality and production efficiency.
Quality control in garment production is a comprehensive and multi-stage process. Through strict control and management at various stages, including pre-production planning and material inspection, in-process monitoring, final inspection and quality assurance, as well as post-production auditing, it is ensured that every garment product meets quality standards and fulfills consumers' needs and expectations.
3. Best practices for ensuring garment quality
In the garment industry, ensuring product quality is crucial for enterprises to win the market and establish brand reputation. To achieve this goal, here are some widely recognized best practices, covering various aspects from production processes to team management.
Implement Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) serve as the cornerstone in garment production, providing a detailed and clear operational framework for every production step. These procedures outline specific operational procedures and establish clear quality expectations, ensuring that each step is executed in accordance with established standards. By implementing SOPs, enterprises can ensure consistency and stability in the production process, reduce human errors and variations, and enhance product quality. Additionally, SOPs serve as quick-start training materials for new employees, aiding them in swiftly integrating into the production environment and enhancing production efficiency.
Train and empower the quality control team
To enable them to identify defects and understand quality benchmarks more effectively, enterprises must invest in training. Through systematic training courses, quality control teams can learn the latest quality control concepts and techniques, enhancing their professional expertise. Enterprises should also empower quality control teams, allowing them to exhibit greater initiative and efficiency during the production process. Quality control teams should have the authority to monitor and inspect the production process, as well as propose improvement suggestions for identified issues and promote their implementation.
Utilize technology to enhance quality monitoring
Artificial intelligence-driven inspection systems and automated measurement tools are two highly effective technological means. Artificial intelligence inspection systems can utilize deep learning algorithms to intelligently identify and analyze clothing, quickly and accurately detecting defects and issues. Automated measurement tools can enhance measurement accuracy and efficiency, reducing human error. By utilizing these advanced technologies, enterprises can improve the accuracy and efficiency of quality monitoring, ensuring that every garment meets quality standards.
Establish clear communication with suppliers
In the garment production process, suppliers are an indispensable part. To ensure that suppliers provide raw materials and accessories that meet quality standards, enterprises must establish strong cooperative relationships with them and provide clear quality requirements. This means that enterprises should communicate fully with suppliers, clarify their own quality standards and expectations, and ensure that suppliers fully understand and meet these requirements. At the same time, enterprises should also regularly evaluate and audit suppliers to ensure that their quality control systems operate effectively and continue to provide high-quality raw materials and accessories.