You play a crucial role in maintaining product safety and quality by performing glass container inspection. This process helps you meet industry standards and protect consumers from harm.
By mastering inspection techniques, you help keep products safe and uphold industry compliance.
Key Takeaways
l Maintain a clean and organized inspection area to enhance focus and reduce the risk of missing flaws.
l Use proper lighting and magnification tools to improve defect detection accuracy during inspections.
l Combine visual, tactile, and technological methods for a comprehensive inspection of glass containers.
l Regularly calibrate inspection equipment and update software to ensure optimal performance and accuracy.
l Document all inspection results to track trends and improve processes for continuous quality assurance.
Glass Container Inspection Preparation
Setting Up the Inspection Area
You need a clean, organized workspace for effective glass container inspection. Remove dust, debris, and unnecessary items from the area. Place inspection tables at a comfortable height to reduce fatigue. Arrange containers so you can access each one easily. Good organization helps you maintain focus and reduces the risk of missing flaws.
Essential Tools and Lighting
Proper lighting is critical for detecting defects. Aim for illumination between 2,000 and 3,750 lux. Use bright LED lamps to reveal cracks, bubbles, or inclusions. Magnification tools, such as handheld magnifiers or digital microscopes, allow you to examine surfaces closely. The table below highlights how lighting and magnification tools improve inspection accuracy across different industries:
| Application Area | Effectiveness | Benefits |
| Jewelry | Increases inspection speed by 20% | Bright LED lighting reveals minute imperfections |
| Electronics Manufacturing | Reduces error rates by 15-25% | Essential for quality control |
| General Use | Compatible with digital devices | Ergonomic designs prevent user fatigue |
Select tools that fit your inspection needs and ensure they are clean and well-maintained.
Safety Measures
Protect yourself during glass container inspection by using appropriate personal protective equipment. You should wear cut-resistant gloves to prevent hand injuries. Safety glasses and goggles shield your eyes from flying debris and chemical splashes. Respiratory masks help you avoid inhaling harmful substances. Hearing protection is important in noisy environments. Choose eye protection with features like scratch resistance, impact protection, and side shields. Make sure your equipment fits comfortably and securely for extended use.
Tip: Always inspect your safety gear before starting work. Replace damaged items immediately to maintain a safe inspection environment.
Step-by-Step Glass Container Inspection
Visual Inspection Methods
You begin glass container inspection by focusing on visual techniques. Industry experts recommend a systematic approach to maximize accuracy and consistency. Follow these steps to inspect each container:
1. Train yourself to recognize defects such as loose caps, cracks, and chips.
2. Set clear criteria for identifying foreign particles and other contaminants.
3. Minimize distractions and background noise in your inspection area.
4. Limit inspection sessions to recommended durations, taking regular breaks to maintain sharp vision.
5. Record the time spent on each inspection to monitor performance and prevent fatigue.
6. Use a matte black or non-glare white backdrop to highlight flaws.
7. Adjust lighting intensity between 2,000 and 3,750 lux, increasing brightness for challenging items.
You can enhance your ability to detect defects by using infrared light sources. Infrared illumination reveals chips and scratches that may be invisible under standard lighting. Defective areas appear darker due to diffuse reflection, making it easier for you to spot flaws on transparent surfaces. High-resolution imaging further improves your ability to identify subtle imperfections.
Tip: Always inspect containers from multiple angles. Rotate each item slowly to catch hidden cracks or inclusions.
Tactile and Functional Checks
Visual inspection alone may not reveal every flaw. You should perform tactile and functional checks to ensure comprehensive glass inspection. Run your fingers gently along the rim, body, and base of each container. Feel for rough edges, chips, or uneven surfaces. These tactile cues often indicate structural weaknesses that visual methods might miss.
Test the container’s functionality by checking for proper sealing and closure. Confirm that caps or lids fit securely and that threads or locking mechanisms operate smoothly. If you notice resistance or misalignment, the container may have a manufacturing defect. You should also tap the glass lightly and listen for clear, resonant sounds. Dull or uneven tones can signal internal cracks or stress points.
Note: Wear cut-resistant gloves during tactile checks to protect your hands from sharp edges.
Using Technology to Detect Defects
Advanced technology has transformed glass container inspection. Machine vision systems act as electronic inspectors, scanning each container for microscopic flaws. These systems use high-resolution imaging and multispectral techniques to highlight defects that human eyes may overlook.
Artificial intelligence modules process images in real time, classifying containers as pass or fail. Deep learning algorithms analyze large datasets, improving defect detection accuracy and providing instant feedback for production adjustments. You benefit from reduced false positives, lower scrap rates, and enhanced adaptability to different container shapes and sizes.
You can rely on these technologies to detect defects with greater consistency and speed. Machine vision systems improve production efficiency and help maintain high standards in glass inspection.
Tip: Regularly calibrate your inspection equipment and update software to ensure optimal performance.
Detect Defects in Glass Containers
Surface and Finish Flaws
You encounter many surface and finish defects during glass inspection. These flaws often appear on the mouth, rim, or outer surface of containers. You must pay close attention to the following types:
| Defect Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Depression (notch) in the mouth | The inner diameter of the bottle mouth is too large, causing potential leakage. |
| Cracked or damaged bottle mouth | Defects in the flange or thread of the bottle mouth due to impact. |
| Rough bottle mouth | Poor finish of the mouth mold, not acceptable for high-quality products. |
| Clamp cracks and bottleneck cracks | Cracks caused by bottle clamps or in the neck of the bottle, usually horizontal. |
You detect defects such as rough finishes, cracks, and depressions by using high-resolution imaging and tactile checks. These flaws can compromise sealing and product safety.
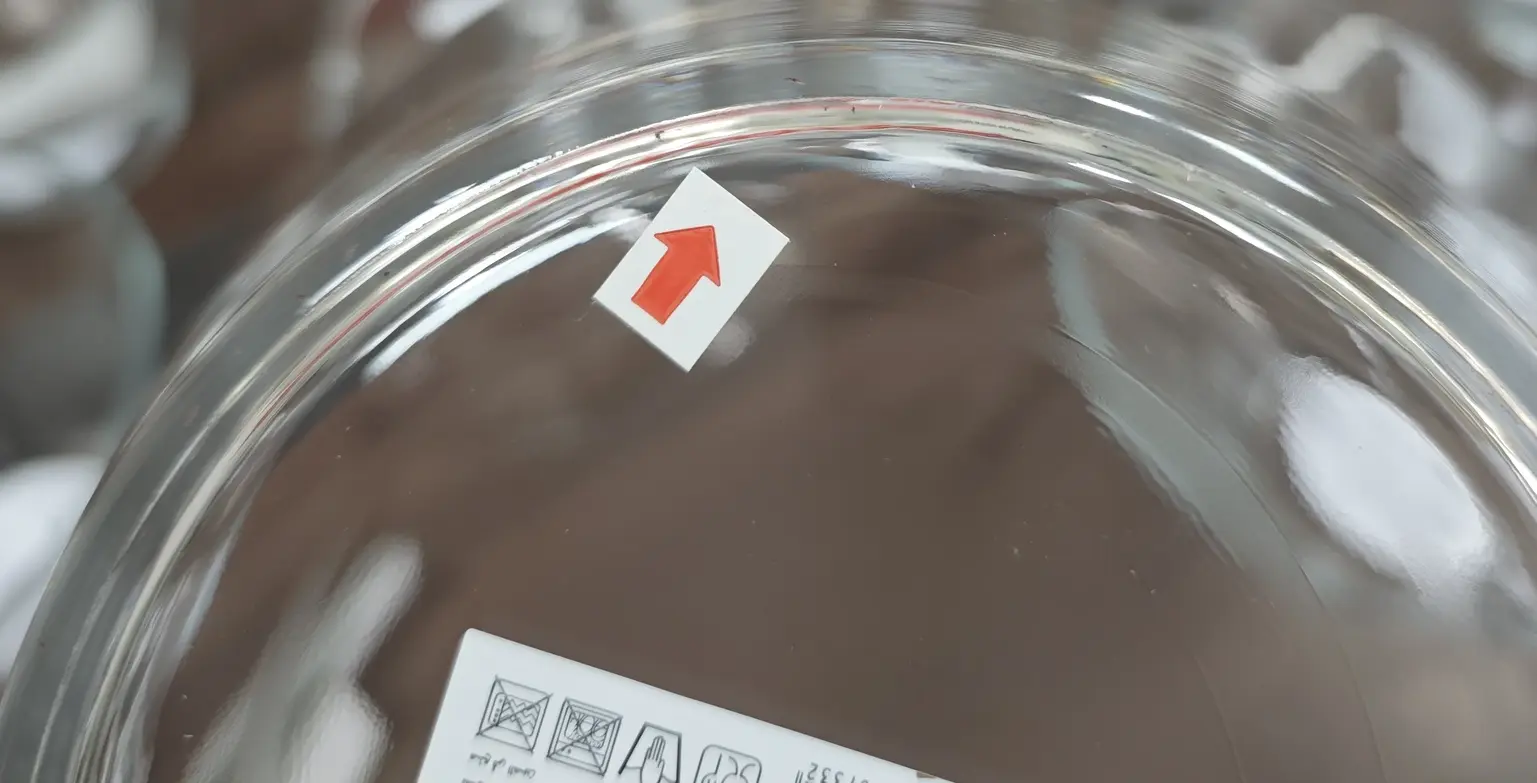

Guess what defect this is?
Body and Base Defects
Body and base defects affect the structural integrity and appearance of glass containers. You should look for the following issues:
- Un-melted raw materials lead to inclusions known as 'Stone' defects.
- Refractory material shedding introduces fragments into the glass, causing stuck ware defect and internal blisters.
- Crystallization during cooling results in visible defects and weak spots.
You identify defects like dented bottles, crack seam lines, and bottles with smaller diameters during glass inspection. These defects can impact labeling, capacity, and overall durability.
Internal and Structural Issues
Internal defects pose serious risks to product safety and shelf life. You must detect defects such as internal blisters and cracks that may not be visible on the surface. The following table highlights how these issues affect container performance:
| Aspect | Impact on Product Safety and Shelf Life |
|---|---|
| Bottle Strength | Prevents package failure during transport and potential consumer injury. |
| Impact Resistance | Ensures containers can withstand mechanical stresses without breaking. |
| Thermal Performance | Addresses risks of thermal shock that can lead to spontaneous fractures. |
| Chemical Durability | Ensures that trace elements do not leach into contents, maintaining product integrity. |
Glass is sensitive to rapid temperature changes, which can cause fractures. This is critical during pasteurization and hot-fill operations. Chemical durability ensures that no harmful trace elements leach into the product, protecting food and pharmaceuticals.
Tip: You improve glass inspection accuracy by combining visual, tactile, and technological methods to detect defects at every stage.
Glass Inspection Best Practices
Consistency and Accuracy Tips
You achieve reliable glass inspection results by following proven quality assurance methods. Start by maintaining a distraction-free inspection area. This environment helps you focus and make clear decisions when identifying defects. Use automated vision systems with high-speed cameras and AI analysis to detect defects in real time. These systems reject non-conforming containers immediately, reducing the risk of human error. Integrate environmental monitoring to track temperature and humidity, which can influence defect formation.
Ongoing training is essential. Regular sessions help you recognize a wide range of defects and improve decision-making consistency. Training programs often include hands-on learning, exposure to modern techniques, and updates on sustainable practices. You should also check your visual acuity regularly, as your ability to spot defects depends on your eye performance. Use inspector aids and physical tools to optimize viewing angles and reduce variability.
Always inspect every container individually. This 100% inspection approach ensures you catch visible contamination or internal defects. Incorporate torque and seal integrity checks to confirm closure tightness and product safety. Document all inspection results, including equipment checks, cleaning effectiveness, and any container breakages. Accurate records help you identify trends and improve your process.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
You can avoid frequent errors in glass inspection by staying aware of common pitfalls. Do not rely solely on visual checks. Some defects, especially internal defects, require tactile or technological methods like high-resolution imaging. Skipping regular equipment calibration leads to missed defects and inconsistent results. Neglecting ongoing training can cause you to overlook new types of defects or changes in product formulation.
Failing to follow regulatory standards can result in serious consequences. For example, the FDA issued advisories about glass lamellae in injectable drugs after several recalls. Glass remains the preferred packaging for pharmaceuticals because it prevents chemical leaching and allows for easy visual inspection. Always keep detailed records to demonstrate compliance and support traceability.
Tip: Use trend analysis from your inspection data to identify recurring defects and adjust your process for continuous improvement.
You ensure product safety and quality by following a structured glass container inspection process. Focus on prevention, optimize your protocols, and train your team to minimize internal defects and other flaws.
Effective glass container inspection protocols focus on prevention rather than traditional inspection methods. By optimizing processes, selecting appropriate materials, and training personnel, manufacturers can minimize defects and ensure product safety. This approach not only protects yield and controls costs but also safeguards patients who rely on life-saving therapies.
- Rigorous inspection practices maintain high-quality products and enhance consumer trust.
- Reliable packaging prevents recalls and supports your brand reputation.
Review your inspection protocols regularly and commit to continuous improvement for long-term success.
FAQ
What are the most common defects you find in glass containers?
You often find cracks, chips, bubbles, and inclusions. Surface flaws like rough finishes or depressions also appear frequently. These defects can affect product safety and quality.
How often should you calibrate inspection equipment?
You should calibrate inspection equipment before each shift or production run. Regular calibration ensures accurate defect detection and maintains consistent inspection standards.
Why is proper lighting important during inspection?
Proper lighting helps you spot small cracks, bubbles, and other flaws. Bright, even illumination between 2,000 and 3,750 lux reveals defects that might be invisible under poor lighting.
Can you rely only on visual inspection for glass containers?
No, you should combine visual, tactile, and technological methods. Some defects hide inside the glass or on surfaces that are hard to see. Using multiple techniques increases detection accuracy.
What records should you keep during glass container inspection?
- Inspection results
- Equipment calibration logs
- Cleaning records
- Details of any defects found
Keeping detailed records helps you track trends and improve your inspection process.
Grow your business with TradeAider Service
Click the button below to directly enter the TradeAider Service System. The simple steps from booking and payment to receiving reports are easy to operate.